
In 2023, the world witnessed a rise in CO2 emissions related to energy by 410 million tons, marking a 1.1% increase. This was a slight decrease from the previous year’s increase of 490 million tons (1.3%). The International Energy Agency (IEA) highlighted the significant role of clean energy technologies, including solar energy, wind, nuclear energy, heat pumps, and electric cars, in curbing the growth of emissions from 2019 to 2023.
- Green Transition Handbook for Businesses
- Promoting sustainable development for businesses
- CBAM mechanism: Companies need to report emissions from electricity consumption
Without the adoption of these clean technologies
Emissions would have tripled. The IEA’s 2023 CO2 emissions report revealed that global energy-related CO2 emissions hit a record high of 37.4 billion tons. The increase in emissions in 2023 was 410 million tons compared to 2022, a 1.1% rise. However, this rise was lower than the 490 million tons (1.3%) increase in 2022. Interestingly, this rate of emission growth was significantly slower than the global GDP growth rate of about 3% in 2023.
A noteworthy point in the report was the record decline in global hydroelectric production in 2023 due to severe and prolonged droughts. This led to an increase of about 170 million tons of CO2 emissions from fossil fuel-fired power plants to compensate. Without this impact, global emissions from the electricity sector would have decreased in 2023.
The IEA emphasized the crucial role of clean energy technologies in reducing emissions. From 2019 to 2023, total energy-related emissions increased by about 900 million tons. Without the increasing adoption of key clean energy technologies since 2019, emission growth would have tripled. This highlights the importance of continuing to invest in and adopt clean energy technologies to mitigate the impacts of climate change.
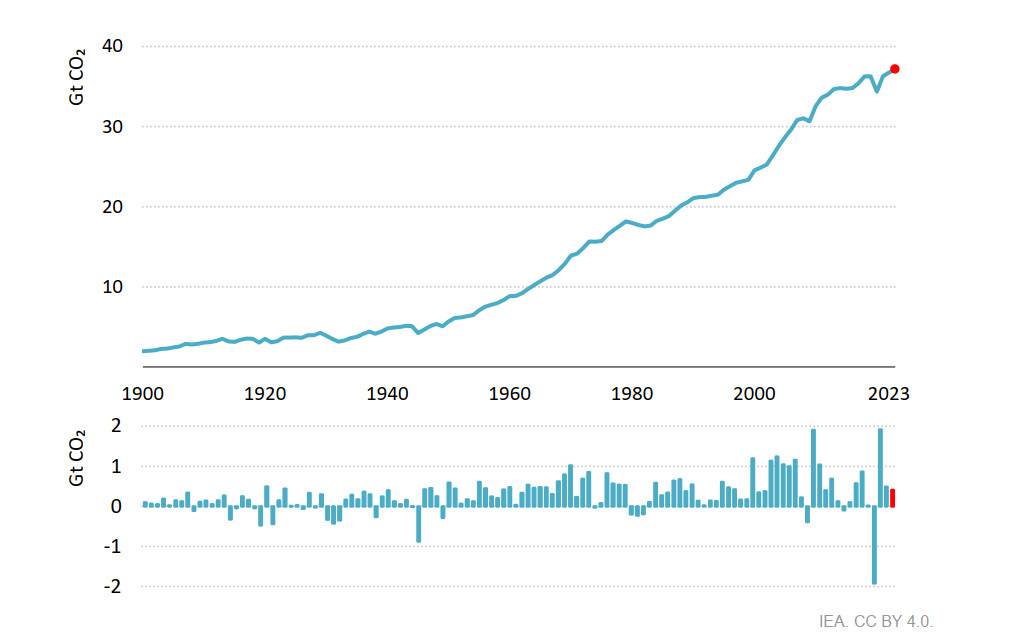 Global energy-related CO2 emissions and annual change over 1900-2023 (Image: IEA)
Global energy-related CO2 emissions and annual change over 1900-2023 (Image: IEA)
Decrease in emissions in advanced economies
According to the IEA report, after a 4.5% reduction in 2023, emissions in advanced economies were lower than 50 years ago – in 1973. Although emissions in these countries had previously reached similar levels in 2020, 1974-1975, and 1982-1983, the difference is that emissions in advanced nations decreased in structure, and the GDP of advanced economies increased by about 1.7% in 2023 – compared to stagnation or complete decline in previous periods. The IEA concluded that 2023 marked the largest percentage decrease in emissions from advanced economies outside of recession periods.
In advanced economies, nearly two-thirds of the emission reduction in 2023 was in the electricity sector, thanks to renewable and nuclear energy production reaching 50% (with renewables alone accounting for an unprecedented share of ~34%). In the European Union, total CO2 emissions from energy combustion processes decreased by nearly 9% in 2023 (equivalent to 220 million tons). The main drivers of this decline were the deployment of renewable energy in the electricity sector, mild weather conditions and reduced industrial emissions.
The United States also saw a decrease in total CO2 emissions from energy combustion by 4.1% (equivalent to 190 million tons), despite economic growth of 2.5%. Two-thirds of the emission reduction came from the electricity sector, with the largest driver being the transition from coal to natural gas. In 2023, due to poor wind conditions and a decrease of about 6% (15 TWh) in hydroelectric production, renewable energy in the electricity sector in the country reduced emissions by about 20 million tons (compared to a reduction of about 40 million tons if these conditions did not occur).
According to Fatih Birol, the IEA’s Executive Director, the clean energy transition has faced intense challenges over the past five years and has proven its resilience. The clean energy transition continues to progress rapidly and contributes to limiting emissions – even as global energy demand increases more in 2023 than in 2022. According to Birol, what is important is that “more effort is needed to create conditions for emerging and developing economies to increase investment in clean energy.“
Vu Phong Energy Group
Read more:









